Budgeting 101: A Beginner’s Guide to Financial Planning
Introduction:
Effective budgeting and financial planning are essential skills that can help individuals and households achieve their financial goals, reduce debt, and build a secure future. If you’re new to budgeting, it’s normal to feel overwhelmed or uncertain about where to start. In this beginner’s guide to financial planning, we will break down the process into simple steps and provide you with practical tips to create a budget that works for you. By mastering the art of budgeting, you can take control of your finances and pave the way for a more secure and prosperous future.
- Assess Your Current Financial Situation:
The first step in budgeting is to assess your current financial situation. Take a comprehensive look at your income, expenses, debts, and savings. Track your expenses for a month to gain a clear understanding of your spending habits. This evaluation will serve as a foundation for creating a realistic and effective budget.
- Set Financial Goals:
Identify your short-term and long-term financial goals. Do you want to pay off debt, save for a down payment on a house, or build an emergency fund? Setting specific and achievable goals will give your budgeting efforts purpose and motivation. Write down your goals and review them regularly to stay focused and motivated. - Create a Monthly Budget:
A budget is a roadmap for managing your income and expenses. Start by listing all your sources of income and categorize your expenses, such as housing, transportation, groceries, utilities, entertainment, and debt payments. Allocate a portion of your income to each category, ensuring that your expenses do not exceed your income. Use budgeting apps or spreadsheets to make the process easier and more organized.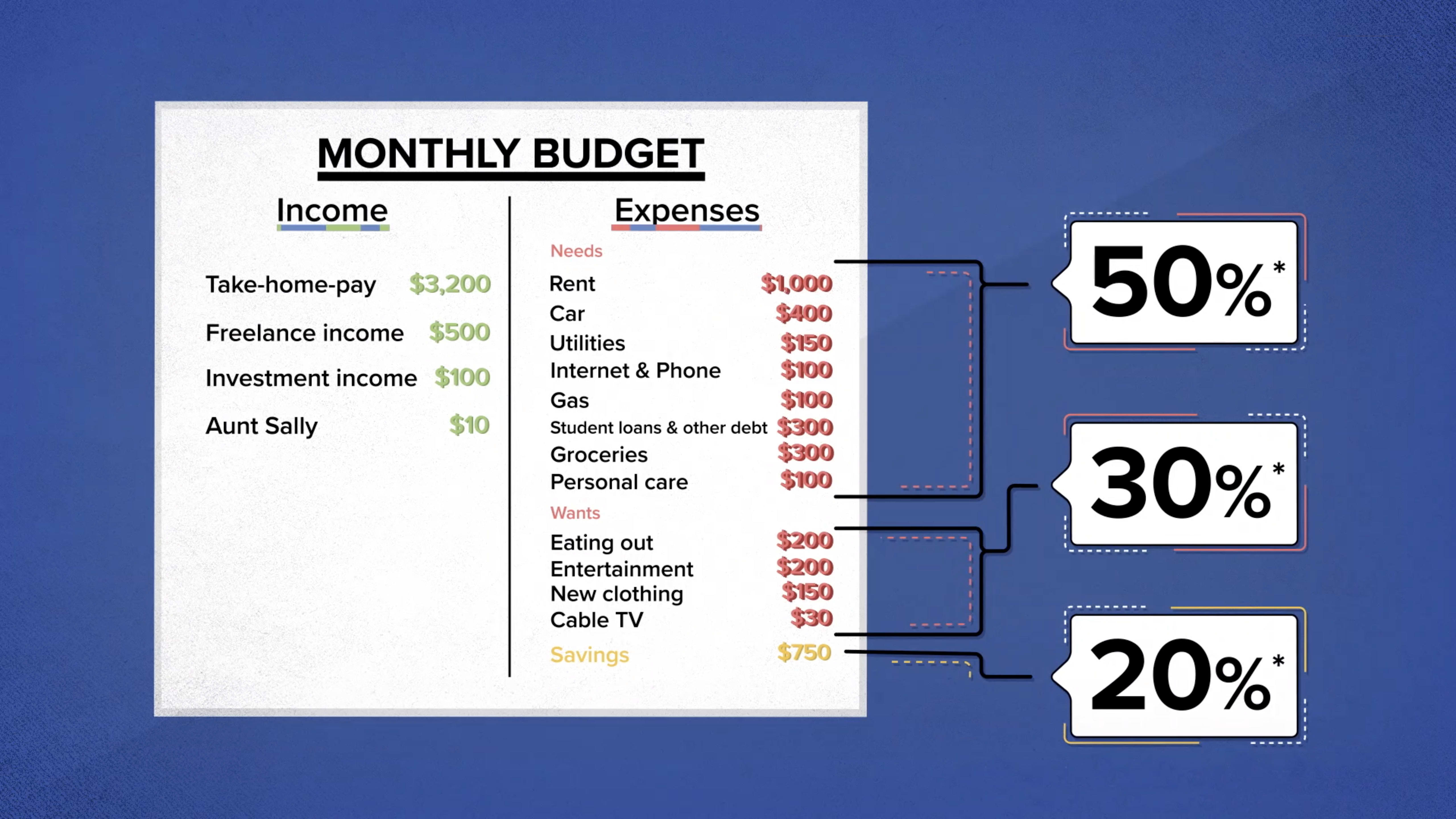
- Prioritize Essential Expenses:
When creating your budget, prioritize essential expenses before discretionary spending. Essential expenses include housing, utilities, groceries, transportation, and debt payments. By allocating funds to these categories first, you ensure that your basic needs are met before considering discretionary expenses. - Track and Monitor Your Spending:
Consistently tracking and monitoring your spending is crucial for successful budgeting. Regularly review your expenses against your budget to identify areas where you might be overspending. Use personal finance apps or online tools to categorize and track your expenses automatically. Being aware of your spending habits will help you make informed decisions and adjust your budget as needed.
- Minimize Discretionary Spending:
Discretionary spending refers to non-essential expenses like dining out, entertainment, and shopping. While it’s important to enjoy life, minimizing discretionary spending can help you free up funds for savings and achieving your financial goals. Look for areas where you can cut back or find more affordable alternatives without sacrificing too much enjoyment. - Build an Emergency Fund:
An emergency fund acts as a safety net during unexpected financial challenges. Aim to save three to six months’ worth of living expenses in a separate savings account. Start by setting aside a small portion of your income each month and gradually increase the amount as your financial situation improves. Having an emergency fund provides peace of mind and reduces the need to rely on credit cards or loans during unforeseen circumstances. - Reduce and Manage Debt:
Debt can hinder your financial progress. Prioritize paying off high-interest debts, such as credit card balances or personal loans. Consider implementing strategies like the debt snowball or debt avalanche methods to accelerate your debt repayment. Seek professional advice if you’re struggling with significant debt to explore options like debt consolidation or negotiating lower interest rates. - Save and Invest for the Future:
In addition to building an emergency fund, it’s crucial to save and invest for your long-term goals. Allocate a portion of your budget to retirement savings accounts, such as employer-sponsored 401(k) plans or individual retirement accounts (IRAs). Explore investment options that align with your risk tolerance and time horizon. Start early to take advantage of compound interest and watch your savings grow over time. - Review and Adjust Your Budget:
Financial circumstances and goals change over time, so it’s essential to regularly review and adjust your budget. Conduct monthly or quarterly reviews to evaluate your progress, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments. A flexible budget allows you to adapt to life changes and ensures your financial plan remains effective.
Conclusion:
Budgeting and financial planning are valuable skills that can lead to financial stability and a brighter future. By assessing your current financial situation, setting goals, creating a monthly budget, tracking expenses, minimizing discretionary spending, building an emergency fund, reducing debt, saving for the future, and regularly reviewing your budget, you can take control of your finances and work towards your financial aspirations. Remember, budgeting is a journey, and with each step, you’re making progress towards a more secure and prosperous financial life.
